Vitamins are organic compounds that are necessary for proper health and cannot be synthesized by the body. By strict definition there are 13 nutrients considered to be vitamins in humans. Below are lists of vitamins, their functions in the body, diseases that occur when they are lacking, and dietary sources of vitamins. There are also lists of RDA, RDI, DRI levels, essential amino acids, essential fatty acids, and obscure vitamins (many of which aren’t really vitamins at all).
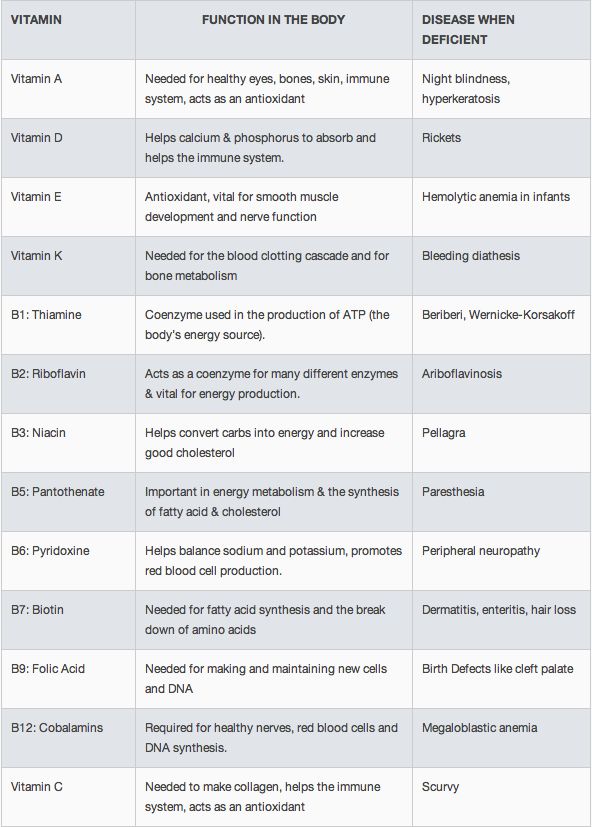
What Vitamins Do in the Body and Vitamin Deficiency
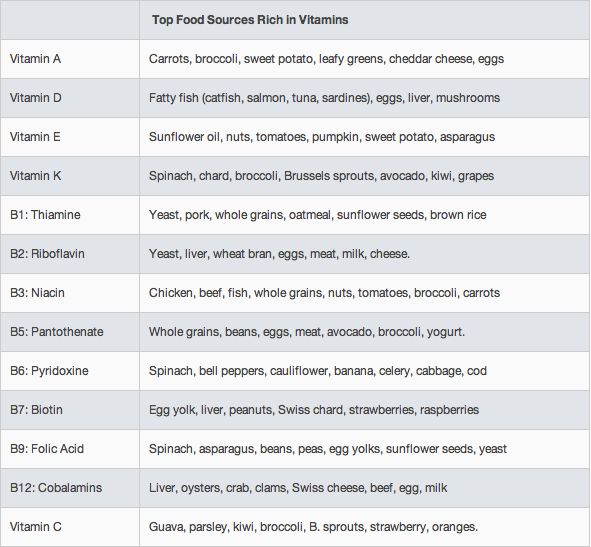
Top Dietary Sources of Vitamins
RDA, RDI, DRI, and UL
The U.S. Recommended Dietary Allowance or RDA was first accepted in 1941 and was revised every five to ten years. The last time it was changed was 1989. The Reference Daily Intake or Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) is the daily amount needed by 98% of individuals in every demographic in the U.S. and is currently used in nutritional labeling. The Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) was introduced in 1997 in order to broaden and update the existing RDA.
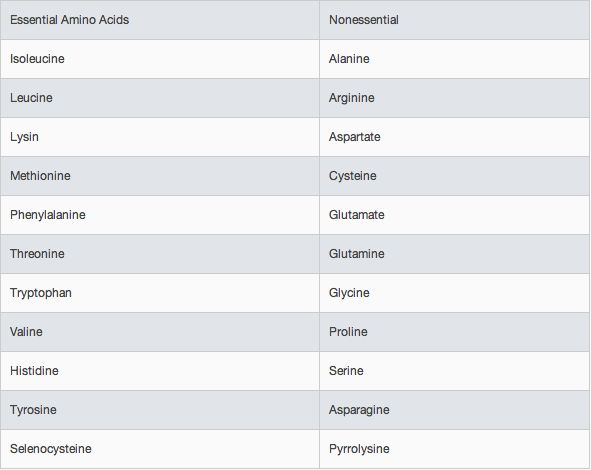
Essential Amino Acids
Amino Acids are the building blocks of protein. Proteins serve multiple functions in the body including making up muscle, hair, nails, and participating in virtually every process within cells.
Essential Fatty Acids
There are only two fatty acids that are considered essential in humans: alpha-linolenic acid (an omega-3) and linoleic acid (an omega-6 fatty acid).
Alpha-linolenic acid is found in high concentrations in flax seed oil, soybean oil, and canola oil. It is useful as a supplement in preventing heart disease, reducing cortisol levels, and neuroprotection.
Linoleic acid is found in cell membranes. Dietary sources rich in linoleic acid include many vegetable oils, and the oils of poppy, safflower, and sunflower seeds.
Vitamin-Like Nutrients or Obscure Vitamin Names
There are other nutrients that are not officially recognized as vitamins. A few of these items are essential, but most are not, and should not make the human essential vitamin list.
- Vitamin B4 or Adenine is a nucleobase.
- Vitamin B8 or Adenosine Monophosphate is also cyclic AMP.
- Vitamin B10 or folate is the basic form of folic acid.
- Vitamin B11 or Pteryl-hepta-glutamic acid or chick growth factor is a form of folic acid.
- Vitamin B13 or Orotic Acid is used to increase the bioavailability of other nutrients.
- Vitamin B14 or Xanthopterine is converted into folic acid by microorganisms.
- Vitamin B15 or Pangamic Acid has no nutritional value nor medicinal use.
- Vitamin B17 or Amygdalin is a glycoside touted as a cure for cancer in the 50’s.
- Vitamin Bc is an outdated name for folic acid (B9).
- Vitamin Bh or Inositol is used in the breakdown of fats and reducing blood cholesterol.
- Vitamin Bp or Choline is an essential nutrient used in making cell membranes.
- Vitamin Bt or L-Carnitine is an amino acid.
- Vitamin Bx or PABA or Para-Aminobenzoic Acid is a precursor to folate in bacteria.
- Vitamin PQQ or Pyrroloquinoline Quinone is taken to support the mitochondria.
- Vitamin F or Linoleic Acid is an essential fatty acid used to make prostaglandins.
- Vitamin G is an outdated name for riboflavin (B2).
- Vitamin H is another name for biotin (B7).
- Vitamin I is an outdated name for biotin.
- Vitamin J or Catechol is an bioflavonoid used in pesticides and perfumes.
- Vitamin L1 or Ortho-Aminobenzoic Acid is an amino acid required for lactation.
- Vitamin L2 or Adenyl Thiomethylpentose is an altered form of L1.
- Vitamin M an outdated name for Folic Acid (B9).
- Vitamin N or Alpha-lipoic acid is an organo-sulfur compound found in almost all foods.
- Vitamin P or Quercetin is a bioflavonoid.
- Vitamin PP is an outdated name for niacin (B3).
- Vitamin Q1 – 10 denote coenzyme Q1 through 10.
- Vitamin R is an outdated name for folate (B10).
- Vitamin S is an outdated name for B11.
- Vitamin T or penicin is a precursor to penicillin derivatives, but itself is not an antibiotic.
- Vitamin U or Methylmethionine is found in alfalfa, cabbage, and cereal grasses.